The Forex fundamentals
The Forex fundamentals
Earning more with leverage: margin, margin call and stop out, equity
Welcome to the third lesson of our Forex Basic course.
In this lesson you will learn:
-
how to use a leverage and earn 500 times more than with your regular investments
-
what a margin is and why a margin call and stop out are not the things you’d like to experience
-
how to calculate your equity and why it is so important.
How to use leverage
During the last decade there have been several major economic events that had a massive effect on the Forex market. For instance, the surprise move by the SNB in January 2015—aka ‘francogeddon’—that caused the Swiss franc to soar by around 30 per cent in value against the euro within minutes.
In October 2016, the British Pound dropped 9% against the US dollar within seconds in overnight trading. The incident was described as a ‘flash crash’.
Such events allow traders to achieve large revenues in a short period of time.
But usually, currency quotes tend to change in a very small percentage.
To earn a tangible amount on Forex, you might have to wait for a next major economic event, invest a huge amount of your personal funds, and ignore all rules of money management.
Luckily, there exists such thing as leverage, and your broker is ready to offer it to you any time you open an order.
Leverage is a loan that multiplies your initial investment and is provided at the moment you open an order.
Leverage is expressed in ratios.
If the leverage is 1:2, it means that you can hold a position twice bigger than your initial investment.
The leverage 1:100 allows you to open positions 100 bigger.
OctaFX offers a wide range of leverage: you can set its amount up to 1:500 depending on your skills and asset you’re trading.
Let’s see how leverage works
Assume you have $2,000 on your trading balance and you wish to invest it in USDJPY without leverage. That enables you to trade 2 micro lots of the pair. You have made a market analysis, checked economic news, and expect the price to raise significantly in the next few days. You open a buy order at the price 110.872 and hold the trade about 37 hours till you close it at 112.482. During that time, the price has increased by 161 pips. The price of a pip, in this case, is $0.09. This way you have earned $28.98. 1.5% of profit is a satisfactory outcome considering the time and funds you’ve put in the trade.
But let’s see what you can get from this trade using the leverage of 1:50.
Your $2,000 allows you to hold $100,000 of capital. That enables you to trade a full-size lot of USD/JPY. Each pip in the pair is now worth $9.09. If you make 161 pips, you earn $1,463. Hence, you have increased your balance by 75%, lifting it to $3,463. You can only achieve such an impressive outcome on the Forex market by applying leverage.
Leverage strengths
Using leverage can be advantageous in two ways:
1. It can help a trader maximise profits per trade.
2. A leveraged trader with limited resources can trade in expensive assets. Without leverage, it would not be viable for a trader with a $1,000 account to trade in gold, which is currently trading at $1,200.
The size of leverage a trader uses is very important in determining the success. When trades go well, a highly leveraged trader can make more money than a trader with lower leverage.
Managing leverage risk
However, do not forget about risks. If you lose 161 pips in your USD/JPY trade, you lose $1,463, and your balance goes down to $537.
Using high levels of leverage, you can quickly double your account, but you can equally fast do the opposite and reduce your account to zero.
That is why you should not invest a substantial part of your balance in one trade no matter how much you could potentially earn. In the trading world, you often hear that leverage is a double-edged sword.
Proper distribution of funds on your balance is called risk management and you will learn about it in our next lessons.
Margin and margin call
To offer you leverage, your broker needs a guarantee that you’re able to cover a potential loss of the trade.
In Forex, this is called a margin, and it is an amount of money required to open and maintain open positions.
Once you open an order, the margin used will be held by a broker until you close your order.
When you open a 1-lot size order with the leverage 1:50 your margin equals $2,000, which amounts to your balance total. Hence, you cannot open new orders until you close this one.
But if you trade 1 mini lot ($10,000) with 1:50 leverage, then, to control that size, you will only need $200.
This way you will have $1,800 left for trading.
Leverage is expressed as a ratio (such as 1:50), while margin is expressed in percentage terms. Your margin makes 2% of the order volume if you apply 1:50 leverage. And your margin only makes 1% of the order volume if your apply 1:100 leverage. Like the leverage ratios, margin requirements vary for different currency pairs.
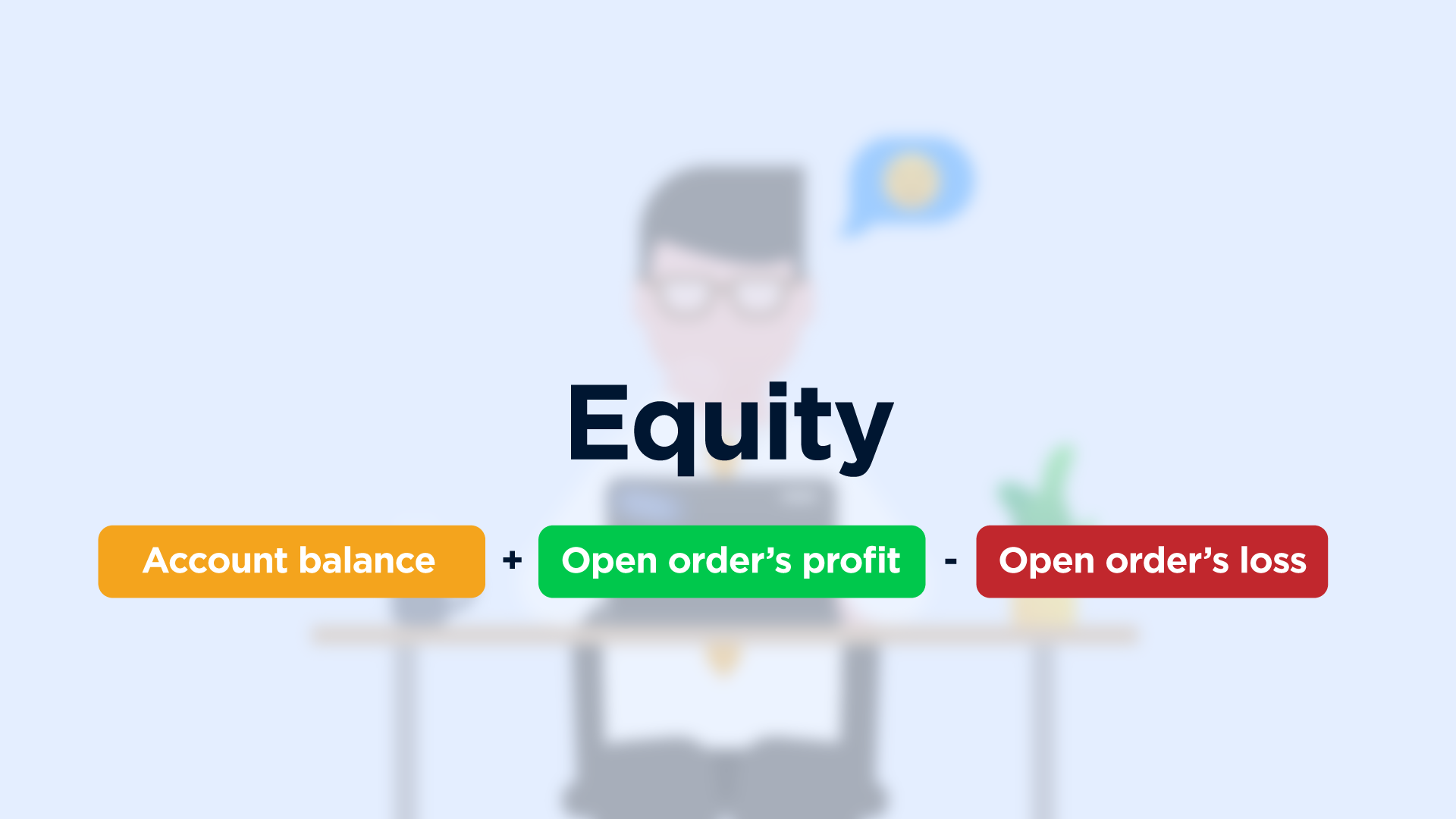
Equity
Assume, you decide to trade mini and micro lots and open many orders.
Good: some of them are profitable and you can get that profit if you close the orders right now.
However, some fruitless order may bring you losses.
If you look at your balance, you will see it still equals $2,000, as it will not change until you close all your open orders.
But how can you track the total outcome of open orders?
For this matter, you need to monitor your account equity.
It represents what your account balance would be if all orders were closed at that time.
Account equity includes your initial investment and floating profit or loss that your open positions have accrued.
Let’s see what you’ve got. It looks like you’ve picked a strategy that works well for you, and the profit that you got from winning orders is bigger than expenses from your lost deals.
Always track your equity. If it gets less than the margin required for all your open orders, you will get a margin call.
Margin call is triggered when the amount of money in your account will soon be not enough to cover your potential loss.
Once it happens, you need either to top up your account balance and increase your equity or to close the position and fix the loss.
If you do not increase your balance after the margin call, stop out will be triggered and your orders will be closed automatically. This way your broker protects you from potential losses that you cannot cover with your own investments.
OctaFX uses balance protection so that you cannot lose more than your initial deposit, even when trading in a highly volatile market.
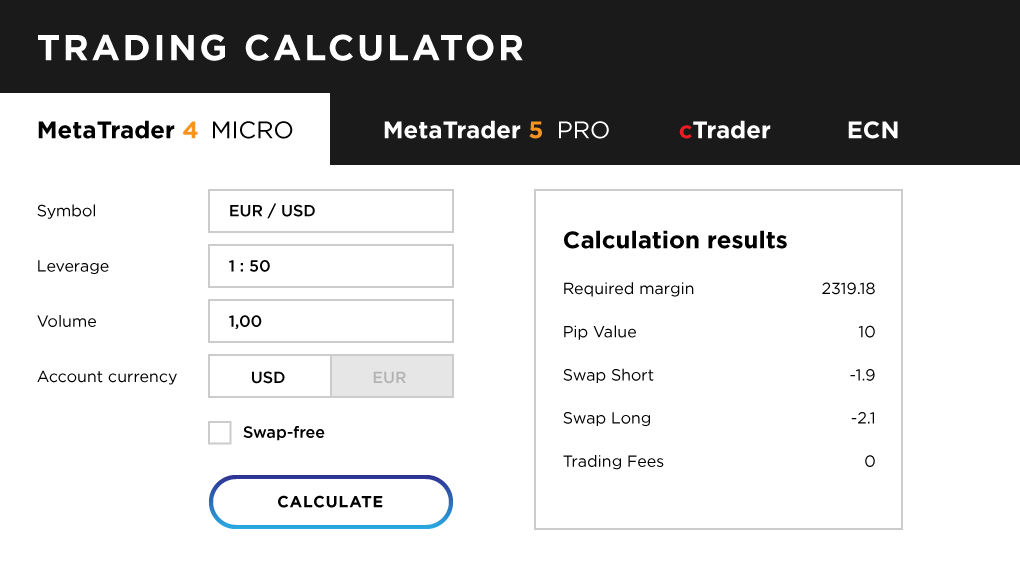
Using the trading calculator on OctaFX, you can see your required margin based on the currency pair you are trading and the amount of leverage you are using. It also shows the pip value for each currency pair.
For example, if you are trading 1 full-size lot in EUR/USD using 1:50 leverage, your required margin is $2,355. In the case of EUR/USD, the calculator shows the value of 1 pip on a full-size lot of EUR/USD, which is $10.
Let’s summarise what we’ve learned from this lesson:
-
Leverage allows you to trade several times larger volumes than you could with your initial deposit. It can multiply your profits but it also multiplies your risks. Leverage is expressed in ratios.
-
A margin is a deposit required to maintain your orders open with leverage. Margin covers potential losses of your trade to a broker.
-
A margin call is a message from a broker, triggered when your losses are about to become bigger than your margin. When you get a margin call you should either close your trade with a loss or add extra funds to your account to support your margin.
-
Stop out is the automatic close of your trade when your losses become equal to your margin. It is required to provide the negative balance protection of your account.
In the next lesson, you will learn:
-
what types of charts you can trade on
-
how to analyze Japanese candles
-
what time frame to choose.